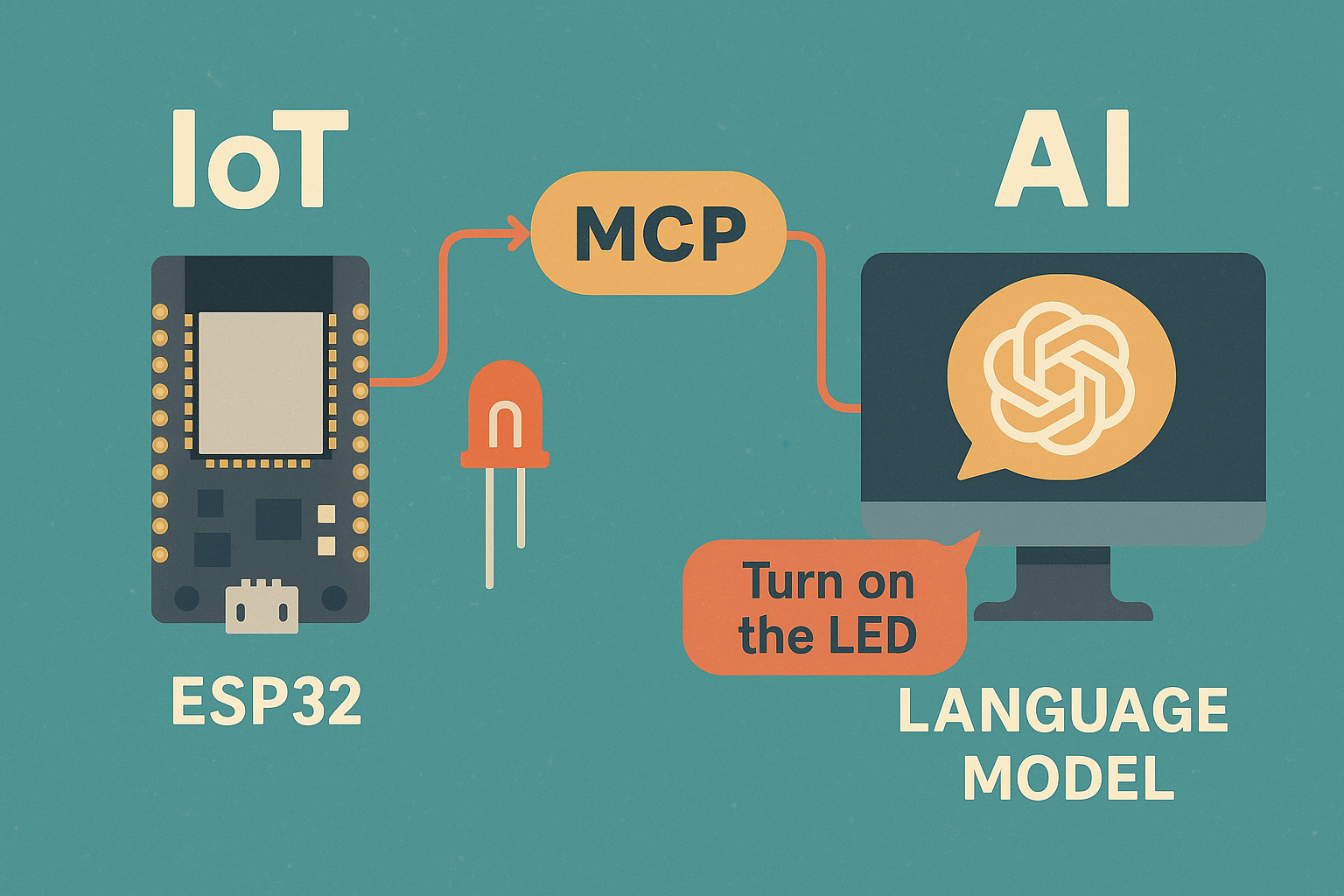
The world of embedded systems is evolving fast — and with it, the need for more powerful, flexible, and secure real-time operating systems (RTOS). Whether you’re building a low-power sensor node, a Matter-ready smart device, or simply want to move beyond Arduino-level projects, Zephyr RTOS offers an incredibly robust foundation.
But it can also seem intimidating at first.
This guide is for makers, developers, and curious tinkerers who want to get hands-on with Zephyr — no prior RTOS experience required. By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have:
- Set up the Zephyr toolchain on your machine
- Built and flashed your first Zephyr application
- Learned how to modify a sample program
- Understood the basics of Zephyr’s modular architecture
Whether you’re using a Nordic nRF52-DK, STM32 Nucleo, or even just running code on a virtual board using QEMU, this guide will walk you through the essentials — step by step.
Let’s get started.
Read more