Have you ever heard of AIoTI?
While browsing for news about the Internet of Things, I recently stumbled upon a headline mentioning AIoTI — and I couldn’t resist digging deeper.
Here’s what I found: in March 2015, the European Commission, together with key players in the IoT space, launched the Alliance for Internet of Things Innovation, also known as AIoTI. Based in Brussels, this unique European association was created to support and strengthen collaboration among IoT stakeholders across the continent.
But the real question is: do we need to know about this?
Is it relevant to us, as makers, tech enthusiasts, or IoT developers?
Absolutely yes.
Everyone should be aware of global organizations like AIoTI. Today, these alliances hold enormous influence, funding, and innovation power. They can take an idea and scale it into something that shapes industries — much like how the fashion world sets trends and colors for the season.
The Internet of Things is quickly becoming part of everything — from factories and cities to homes, gadgets, and wearables. Soon, it will be as embedded in our lives as smartphones and social media.
The European Commission’s goal with AIoTI is to foster a dynamic, open IoT ecosystem — one that can unleash the full potential of IoT technology. Built on the earlier work of the IoT Research Cluster (IERC), AIoTI aims to share innovation across industries, helping transform fresh ideas into practical solutions and sustainable business models.
Who are the AIoTI?
Members of the Alliance include key IoT industrial players – large companies, successful SMEs and dynamic startups – as well as well-known European research centers, universities, associations and public bodies. The most important members and founders are Philips Lighting, Vodafone, IBM, ATOS, BT, John Deere, Infineon, Engineering LOI, CNH Industrial, Telit Communications, Siemens, Bosch, Huawei, Nokia Artemisia, Digital Catapult, Gradiant, Samsung, STMicroelectronics, Schneider Electric, and Arthur’s Legal.

The AIoTI as a legal entity maintains a close partnership with the European Commission on policy recommendations and on building the strategy for the research and innovation agenda for the future IoT funding programme.
Structure and Working Groups target
➔ Innovation Ecosystems
This Working Group aims at designing actions to develop innovation ecosystems by stimulating startups, encouraging the use of open IoT platforms, enabling Large Scale Pilots, and linking large and small companies through open innovation.
➔ IoT Standardization
This Working Group identifies and, where appropriate, makes recommendations to address existing IoT standards, analyses gaps in standardization, and develops strategies and use cases aiming for (1) consolidation of architectural frameworks, reference architectures, and architectural styles in the IoT space, (2) (semantic) interoperability and (3) personal data & personal data protection to the various categories of stakeholders in the IoT space.
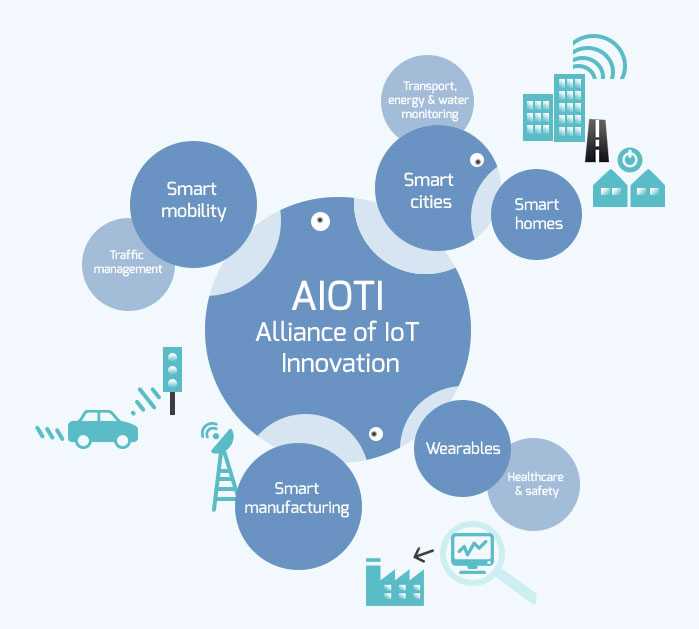
➔ Smart living environment for ageing well
Smart living environment for ageing well: The topic for this Working Group refers to smart homes and smart living environments that can support vulnerable people, such as, but not limited to elderly or disabled people, in staying active, independent and out of institutional care settings, also leading to reduced costs for care systems and better quality of life for vulnerable categories of citizens. The workgroup deliverables include white papers, recommendation reports, innovative use cases susceptible to improve the quality of life of Elderly people using the latest IoT technologies.
➔ Smart Farming and Food Security
The Topic of this Working Group refers to IoT scenarios/use cases that allow monitoring and control of the plant and animal products life cycle “from farm to fork”.
➔ Wearables
The topic for this Working Group refers to IoT solutions that integrate key technologies (e.g. nano electronics, organic electronics, sensing, actuating, communication, low power computing, visualisation and embedded software) into intelligent systems to bring new functionalities into clothes, other fabrics, patches, watches and other body-mounted devices. The Working Group focuses its work on healthcare, well-being, safety, security and infotainment applications.
➔ Smart Cities
The topic for this Working Group refers to IoT solutions used by a city in order to enhance performance, safety and wellbeing, to reduce costs and resource consumption, and to engage more effectively and actively with its citizens. Key ‘smart city’ sectors may include transport, energy, healthcare, lighting, water, waste and other city related sectors.
➔ Smart Water Management
The topic for this Working Group refers to IoT solutions that improve water management efficiency by monitoring and controlling surface water retention, flooding etc.
➔ Smart Energy
The topic for this Working Group refers to IoT solutions deployed by various companies along the value chain (i.e. IoT technology providers, energy companies (in generation, supply, grid and market participants, traders, aggregators, etc.) to allow the performance optimisation of their energy asset portfolios (Renewables plants, Grid Substations, Control Rooms, Prosumer Demand Responsive Loads and EV Charging infrastructures).
➔ Smart Buildings and Architecture
The topic of this Working Group is the IoT technologies and solutions deployed in buildings and districts of buildings to improve life of the occupant by addressing and optimising elements such as comfort, light, temperature, air quality, water, nourishment, fitness, and energy usage.
The Internet of Things Leading Landscape
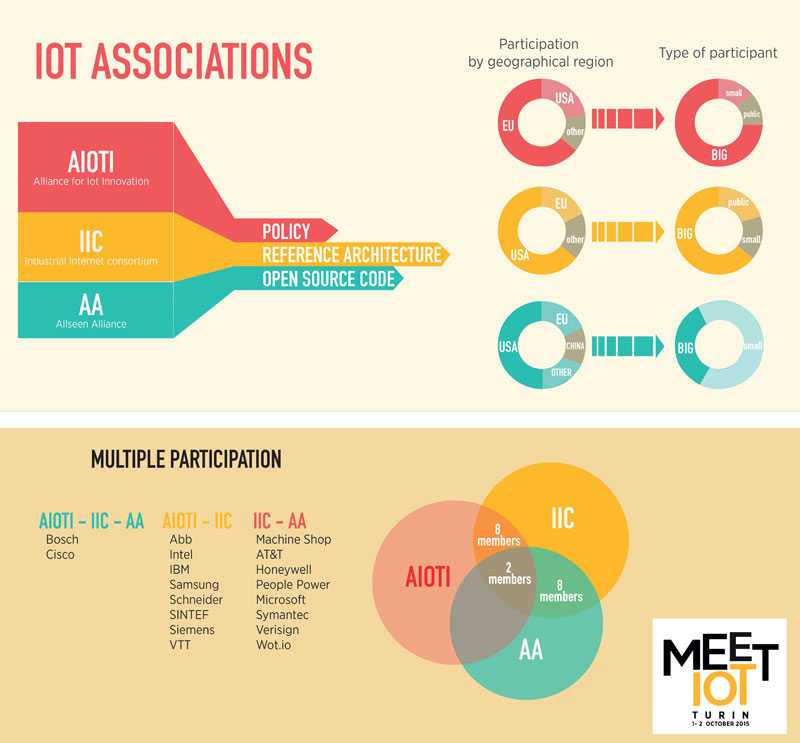
In the past years many industrial alliances and consortia got visible in the global overview but at the first glance they seem to compete over the same topics. However, there are major differences when you take a closer look, at least when talking about he major groups like Allseen Alliance, Industrial Internet Consortium and AIoTI.
The AllSeen Alliance manages the AllJoyn open source project with software code using open standards to enable all the ‘things’ in the Internet of Things to work together. This Alliance started a few years ago, when the Alljoyn protocol was developed by Qualcomm. Now
the management has been given to the Linux Foundation, and target devices belongs to Connected Home, Smart TV, Smart Audio, Broadband Gateways, and Automotive domains. Currently, it has 6 working groups: Common Frameworks Working Group, Compliance and
Certification Working Group, Core Working Group, Developer Support Working Group, Gateway Working Group, and Smart Spaces Working Group.
The Industrial Internet Consortium is just over a year old. It started from 5 major corporations (M, Cisco, AT&T, GE and Intel) and now comprises a large number of partners. Its vision is to develop a Reference Architecture for the IoT that can be exploitable by major Industrial Groups, particularly in the Manufacturing field. It has 18 groups: Marketing, Framework, Use Cases, Data Management and Analytics, Security, Liaisons, Architecture, Communication, Analytics, Architecture Control, Clean Slate, Energy, Ignite,Vocabulary, Interoperability, Positioning, Technology and Thought Leadership.
The newest group is the Alliance for IoT Innovation (AIoTI). Promoted by the European Union, the Alliance is to help the European Commission prepare future IoT research and innovation, standardization and policy. At present it has 11 Working Groups: IoT European research cluster, Innovation Ecosystems, IoT Standardization, Policy issues (trust, security, liability,
privacy), Smart living environments for ageing well (e.g. smart house), Smart farming and food security, Wearables, Smart cities, Smart mobility (smart transport/smart vehicles/connected cars), Smart environment (smart water management), Smart manufacturing.
Note: This is an informative article. Most of the content was inspired from the following sources: www.aioti.org , www.meet-iot.eu, www.ec.europa.eu. Credit for extracted text and images goes to authors.
Hoping that this article inspired you, I kindly invite you share this article, subscribe my YouTube channel and join the communities on social networks. Feel free to comment or send suggestions / remarks so i can improve the content quality.